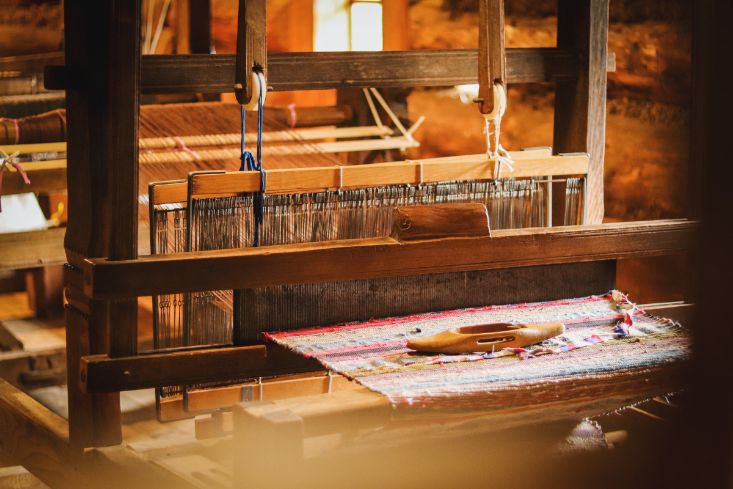
The secondary motions of the looms are the:
- Let off motion:
- Take up motion:
The tertiary motions of the loom are:
- Warp stop motion
- Weft stop motion
Weaving can be summarized as a repetition of these three actions, also called the primary motions of the loom.
- Shedding: The process where the warp up threads ends gets separated by raising or lowering healed frames to form a visible space where the pick can pass.
- Picking: The process where the weft or pick is propelled across the loom by hand, an air-jet, a rapier, or a shuttle.
- Battening: The process where the weft is pushed up against the fell of the cloth by the reed.